- P
- O
- W
- E
- R
- D
- I
- S
- T
- I
- R
- B
- U
- T
- I
- O
- N
Intelligent power distribution – distributed power charger

- Provide variable output (Rather than a fixed, even distribution)
- Intelligently distributes power based on the vehicle's battery status
- Efficient power management with simultaneous/sequential charging

- Patent No.10-1009485
-
Patent for variable capacity (power)
according to the number of charging packs installed
/ Original patent for separated charger with separate power and charging parts
- Power management
-
- Efficient power management (ability to select charging mode based on vehicle capacity)
- Up to 75% power savings compared to existing integrated chargers through customized power control
- Reduced failure rate through simplified and modularized components
- Cost reduction / Ease of expansion
-
- 1:N power bank/dispenser configuration - expandable (1 power bank - up to 50 dispensers)
- Saves 50% of the investment of a conventional installation costs and avoids excessive generation of standby power
- Power bank separation reduces dispenser size, maximizes charging efficiency, and increases capacity for expansion (shared use of general parking spaces)
Comparison of integrated vs. distributed type (Receiving capacity 480kW / 240kW)
480kW Power Receive
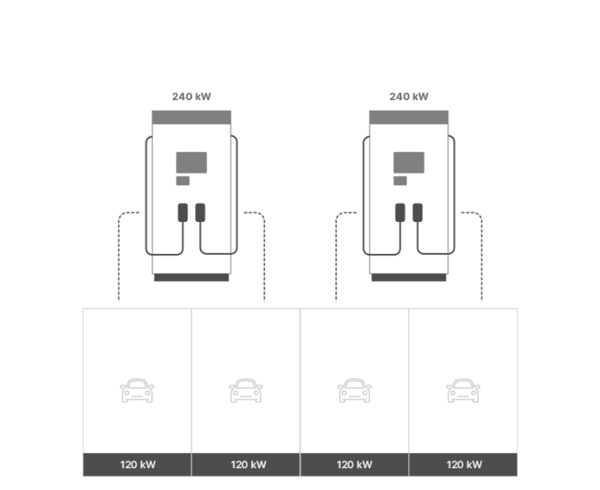

- Embedded Charger
-
- Proportional to the capacity and volume of the charger
-
Installation/receiving capacity according to the charger capacity
(higher cost compared to distributed type)
240kW Power Receive
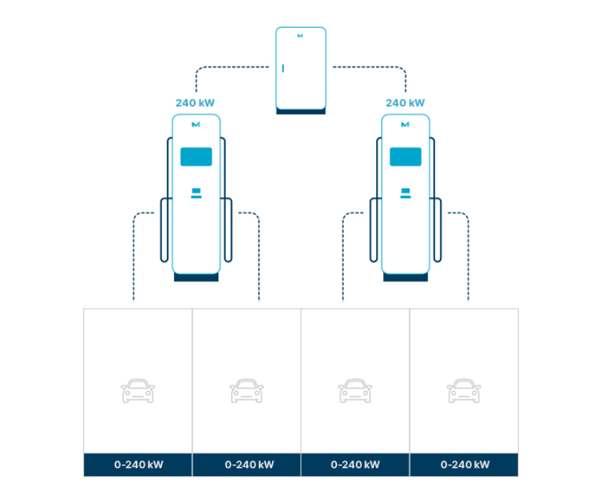

- Separated Charger
-
- Installation space is minimized by separating the power bank
- Peak power distribution technology (a technology that complies with enhanced ESG standards) is a technology that received an ‘S grade’ in the climate valuation by the Korea Institute of Energy Research, reduces operating costs by 50%.
simultaneous and sequential charging
Sequential +
Simultaneous
Charging
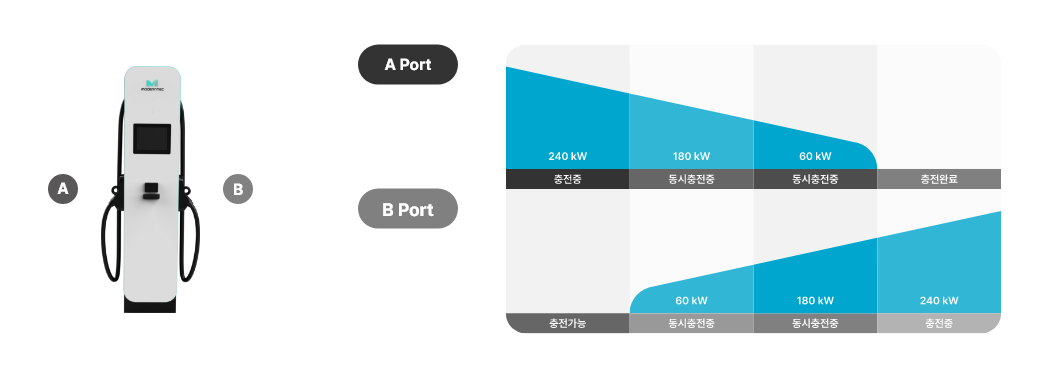
Simultaneous
Charging

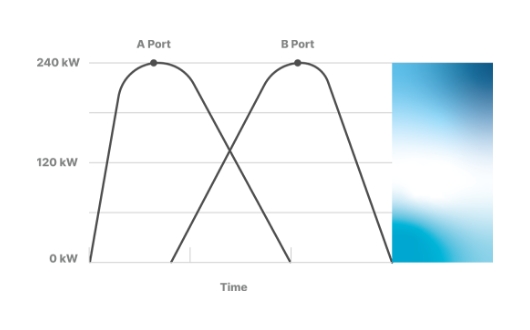
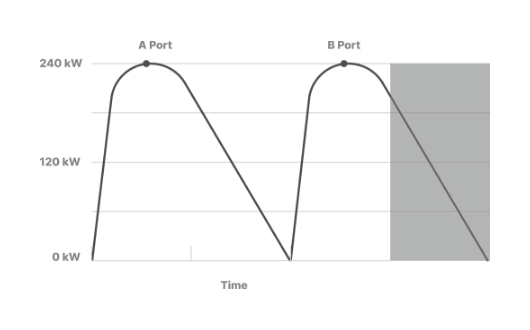
Basic concepts of simultaneous and sequential charging
- simultaneous
charging -
- Complete 70~80% of the vehicle battery charge at port A
- After 70~80% charging, reduce the charger output at the request of the vehicle
- Start charging at port B with idle power due to power reduction
- Maximize operating rate and increase operating profit by reducing the time required for full charging
- Improve management efficiency and easy to install chargers through power distribution system
- Cost reduction by minimizing electricity receiving costs, installation costs, and standby power
- sequential
charging -
- Charging of Port A is completed
- Charging of Port B starts automatically (sequential charging)
- Use of late night hours when electricity costs are the lowest
- Synergistic benefits for transportation and courier companies where late-night charging is essential
- Reduced labor costs for vehicle charging and moving fully charged vehicles
Example of peak management of charging stations in intelligent power distribution, compared to integrated charging
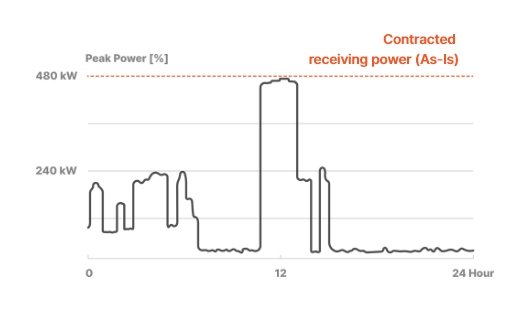
- General charging [low operating rate compared to facility capacity]
-
- Multiple chargers in a site is doomed to bear the tantamount increase of contract power and thus, expensive but inefficient bills
- Power use is patternized to peak at certain times of a day while close to dormant at the rest
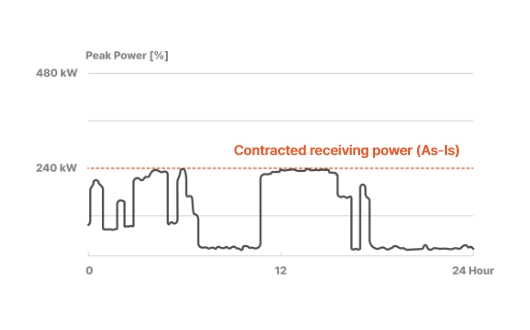
- Intelligent charging [Optimizing the operational efficiency of facility capacity]
-
- Reduced the amount of per site demand power (as low as 50%)
- Stabilize power supply and demand through peak power management
- Provide preliminary grid investigation and operation plan suitable for the particular site
ALL-IN-ONE
 A perfect charging solution is provided
through rapid, medium, and slow integrated
charging modes and intelligent simultaneous
and sequential charging.
A perfect charging solution is provided
through rapid, medium, and slow integrated
charging modes and intelligent simultaneous
and sequential charging.
A single dispenser compatible with all charging speed (slow to fast)